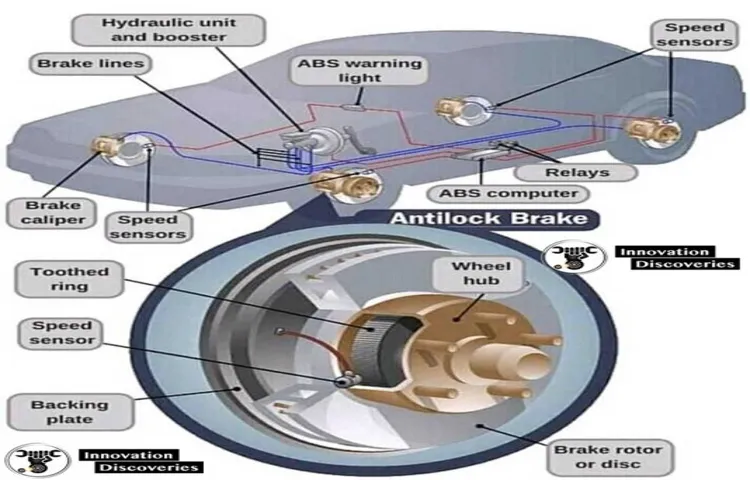
Have you ever wondered how your car’s antilock brake system (ABS) works? It’s a pretty incredible feat of engineering that allows you to brake safely in difficult driving conditions. Essentially, ABS helps prevent your wheels from locking up when you slam on the brakes too hard, thus maintaining traction and steering control. But how does it actually work? Think of it like a dance between your car’s computer, sensors, and hydraulic system.
Together, they work to monitor and adjust your braking pressure hundreds of times per second, all while you focus on staying safe on the road. In this blog post, we’ll delve deeper into the fascinating world of ABS and break down exactly how it keeps you and your passengers secure while driving.
The Importance of Tire Pressure Monitoring
When it comes to maintaining vehicle safety, tire pressure monitoring plays a crucial role. Many modern vehicles come equipped with an antilock brake system (ABS) that also includes tire pressure monitoring functionality. This system utilizes sensors within each tire to track and report on the pressure levels in real-time.
By doing so, the ABS can detect any instances of low pressure or punctures, alerting the driver to take action and prevent further damage or accidents. The specific part of the ABS used for tire pressure monitoring is the wheel speed sensor. Its job is to detect changes in the wheel’s motion and relay that data to the ABS control module.
From there, it can determine if tire pressure is low or if there is a puncture. In addition to ensuring safe driving, maintaining proper tire pressure can also improve fuel efficiency and extend tire life. So, if your vehicle comes equipped with tire pressure monitoring functionality, it’s best to use it to its full extent and stay safe on the road.
The Components of Antilock Brake Systems
Tire pressure monitoring is an essential component of modern vehicles, especially when it comes to safety. Maintaining proper tire pressure is crucial, not only for extending tire life but also for ensuring optimal stopping performance. When the tire pressure is too low or too high, it can lead to uneven wear and tear, improper tire traction, and decreased stopping power.
That’s where tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) come into play. They monitor the air pressure in each tire and alert the driver when a tire’s pressure falls outside of the recommended range. By doing this, TPMS help drivers avoid accidents by reducing the risk of tire blowouts, skids, and hydroplaning.
In summary, TPMS is an important feature that ensures tire safety and contributes to overall road safety.
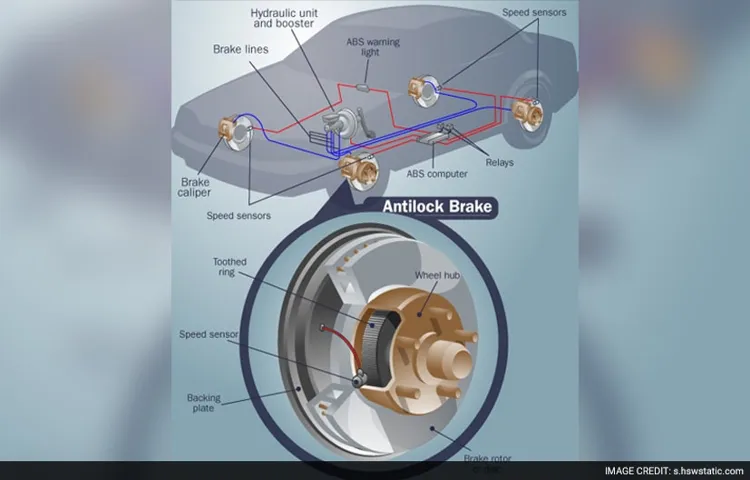
The Role of the Wheel Speed Sensor
As a driver or owner of a vehicle, it’s important to understand the role of the wheel speed sensor. This component is responsible for monitoring the speed of each wheel and sending that information to the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU). This information is crucial for various vehicle systems, including the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and the traction control system.
The ABS relies on the wheel speed sensor to detect any discrepancies in wheel speed and apply the brakes as necessary to prevent the wheels from locking up. Similarly, the traction control system uses this information to adjust power distribution to the wheels, ensuring maximum traction and stability.Another crucial system that relies on accurate wheel speed information is the tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS).
This system alerts drivers when tire pressure falls below the recommended level, which is important for both safety and fuel efficiency. If the wheel speed sensors detect a drop in wheel speed, the TPMS will alert the driver to check the tire pressure and inflate the affected tire. In this way, the wheel speed sensor plays a key role in promoting proper tire maintenance and preventing accidents due to underinflated tires.
In conclusion, the wheel speed sensor is a critical component of any modern vehicle, ensuring the safety and efficiency of various systems, including the ABS, traction control, and TPMS. By monitoring the speed of each wheel and communicating that information to the ECU, the wheel speed sensor helps prevent accidents and promote proper tire maintenance. So, the next time you hit the road, take comfort in knowing that this tiny sensor is hard at work keeping you safe and secure.
The Function of the Tire Pressure Monitor
Tire Pressure MonitorHave you ever wondered why your car has a Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS)? The TPMS is a crucial component of your vehicle’s safety equipment because it warns you when your tire pressure drops below a safe level. Low tire pressure can cause several problems, including reduced fuel efficiency, decreased tire lifespan, and poor handling.The TPMS is designed to keep track of your tire pressure and alert you when it falls below the recommended level.
This way, you can take appropriate action by inflating your tires or seeking professional help if necessary. The TPMS can also help you save money by improving fuel economy, reducing tire wear, and preventing blowouts that can damage your car or cause accidents.Having a TPMS system installed in your car not only ensures your safety but also helps you save money in the long run.
Checking your tire pressure regularly can be a hassle, and the TPMS takes care of this for you by keeping track of your tire pressure and alerting you when necessary. So, if you have a TPMS system in your car, make sure you heed its warnings, and if you don’t, consider getting one installed for your safety and peace of mind.
How Tire Pressure is Monitored
If you’re wondering which part of an antilock brake system is used for tire pressure monitoring, the answer is the wheel speed sensors. These sensors are typically found at each wheel and are responsible for detecting the speed of rotation. When the tire pressure drops below a certain level, the diameter of the tire will decrease, causing the wheel to rotate faster than the others.
The wheel speed sensor detects this variance and sends a signal to the vehicle’s onboard computer, which triggers the tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) warning light on the dashboard. It’s important to ensure that the wheel speed sensors are functioning correctly to ensure accurate tire pressure monitoring. Regular maintenance checks are recommended to ensure that the TPMS is operating optimally to keep you safe on the road.
Maintaining proper tire pressure not only enhances fuel efficiency and prolongs the life of your tires but also improves handling and ultimately makes your driving experience safer and more enjoyable.
Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
Direct Tire Pressure Monitoring SystemsDirect Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) consist of sensors that are installed within the tires of a vehicle to monitor the tire pressure in real-time. The sensors continuously measure the air pressure within the tires and transmit the data wirelessly to a receiver that is located in the vehicle’s onboard computer. The onboard computer displays the tire pressure readings on the dashboard, enabling the driver to know the exact pressure levels of their tires.
Direct TPMS is highly effective, accurate, and reliable, making it an essential safety feature in modern-day vehicles. With proper tire pressure monitoring, drivers can prevent tire blowouts, reduce fuel consumption, and improve the overall performance of their vehicles. Additionally, direct TPMS ensures that the driver maintains adequate tire pressure, which not only enhances safety but also increases the lifespan of the tires.
Having a Direct TPMS system in your vehicle is like having a personal tire doctor, always keeping your tires healthy and ensuring a smooth and safe ride.
Indirect Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
Tire Pressure Monitoring SystemsIndirect Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems operate through the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). The system uses the wheel speed sensors to monitor tire pressure. When a tire loses air, its diameter gets reduced, which changes the rotational speed.
This change is detected by the system, which triggers a warning signal in the dashboard. Additionally, the system also considers variables such as external temperature and internal tire temperature, which could affect tire pressure. Even though indirect systems are less accurate than direct systems, they offer a cost-effective solution for monitoring tire pressure.
They are installed in many vehicles, and they effectively monitor tire pressure without requiring additional hardware. However, their accuracy may vary depending on driving conditions and other factors. It is always best to monitor tire pressure regularly and ensure it is within the recommended range.
Combination Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
Tire pressure monitoring systems have become standard in most cars today. One such system is the Combination Tire Pressure Monitoring System (CTPMS). This system uses multiple sensors, typically four, that are placed inside each tire to monitor air pressure and temperature.
These sensors transmit data wirelessly to a receiver in the car, which displays the information on the dashboard. The CTPMS is much more accurate than traditional systems because it provides live, real-time data about the tires’ conditions. By monitoring the tires’ temperature and pressure, the CTPMS can warn the driver of potential issues before they become dangerous.
Additionally, the CTPMS helps maximize fuel economy by ensuring tires are properly inflated, leading to less drag and better handling. With the CTPMS, drivers can rest assured that their tires are performing optimally.
Conclusion
So in summary, while the antilock brake system may seem like an unlikely candidate for tire pressure monitoring, it actually plays a crucial role in detecting changes in wheel rotation speed that can indicate a decrease in tire pressure. Just like how a good driver keeps an eye on their tires, the antilock brake system works tirelessly behind the scenes to help ensure our safety on the road. Who said brake systems can’t multitask?”
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a tire pressure monitoring system in an antilock brake system? A: A tire pressure monitoring system is used to alert the driver when tire pressure is below the recommended level.2. How does a tire pressure monitoring system function in an antilock brake system? A: A tire pressure monitoring system uses sensors to measure tire pressure and sends this data to the vehicle’s onboard computer. If the pressure is too low, the driver is alerted via a warning light.3. What happens if the tire pressure monitoring system fails in an antilock brake system? A: If the tire pressure monitoring system fails, the driver may not be aware of low tire pressure, which can lead to decreased vehicle performance and potential safety hazards.4. Is a tire pressure monitoring system required by law in antilock brake systems? A: Yes, tire pressure monitoring systems are required by law in all new vehicles equipped with antilock brake systems.5. Can a tire pressure monitoring system be retrofitted to an older vehicle with an antilock brake system? A: Yes, it is possible to retrofit a tire pressure monitoring system to an older vehicle, but it may require aftermarket parts and installation processes.6. Are there any maintenance requirements for a tire pressure monitoring system in an antilock brake system? A: Yes, it is important to regularly check tire pressure and inspect the sensors and wiring for damage or wear.7. Can a faulty tire pressure monitoring system affect the overall safety of an antilock brake system? A: Yes, a faulty tire pressure monitoring system can lead to decreased vehicle performance and potentially unsafe driving conditions.