Welcome to our blog! Today, we are diving into the fascinating and ever-evolving world of introductions. Whether it’s a first impression, a book or movie opener, or even an icebreaker at a social gathering, introductions play a crucial role in capturing our attention and setting the tone for what lies ahead. Just like a captivating prologue in a novel, a well-crafted introduction has the power to ignite curiosity, forge connections, and draw us in.
So, what makes a great introduction? What are the secrets to crafting an opening that leaves a lasting impression? Let’s unpack the art of introductions and discover how they can make or break an experience.
Table of Contents
What is a power inverter?
Power inverters are devices that convert DC (direct current) power into AC (alternating current) power, allowing you to use electronic devices that require AC power from a DC power source, such as a car battery or a solar panel. But how exactly does a power inverter work? Well, think of it as a translator between different languages. DC power is like speaking one language, while AC power is like speaking a different language.
The power inverter takes the DC power and translates it into AC power so that your electronic devices can understand and use it. It does this by using electronic components such as transistors and capacitors to switch the flow of current back and forth, creating a waveform that mimics the AC power from the grid. This waveform is then sent to the outlet where you can plug in your devices.
So, in a nutshell, a power inverter acts as a bridge between DC and AC power, allowing you to power your electronic devices wherever you are.
Definition of a power inverter
power inverter, definition of a power inverter
Importance of power inverters
power inverters
How does a power inverter work?
Many of us rely on electronic devices and appliances in our everyday lives, whether it’s charging our phones or powering our laptops. But have you ever wondered how these devices work when there’s no electrical outlet nearby? That’s where a power inverter comes in. A power inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
Let me break it down for you. DC is the type of electricity that is stored in batteries or comes from sources like solar panels, while AC is the type of electricity that is used in homes and buildings. So, when you plug a DC power source into a power inverter, it uses electronic circuitry to convert that DC electricity into AC electricity.
This allows you to use AC-powered devices and appliances even when you don’t have access to an AC outlet. Think of it like a translator. The power inverter takes the language of DC electricity and translates it into the language of AC electricity so that your devices can understand and use it.
Power inverters can vary in size and capacity, depending on the amount of power they can provide. Some are small enough to fit in your car’s cigarette lighter socket and power small devices, while others are large enough to power an entire house during a power outage. So, the next time you find yourself in need of electricity but without an outlet in sight, remember that a power inverter can come to the rescue, translating DC power into AC power and keeping your devices running smoothly.
Conversion of DC to AC
power inverter, DC to AC conversion, how does a power inverter work Have you ever wondered how you can convert the power from your car battery into usable AC power for your electronic devices? That’s where a power inverter comes in. A power inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) power into AC (alternating current) power, allowing you to run appliances and electronics that typically require AC power. So how does a power inverter accomplish this? Well, let’s start with the basics.
DC power flows in one direction, while AC power oscillates back and forth. The power inverter takes the low voltage DC power from your car battery and uses electronic circuitry to convert it into high voltage AC power. This is done through a two-step process.
First, the DC power is converted into AC power at a high frequency, typically in the range of tens of thousands of hertz. This is done using transistors, which rapidly switch on and off to create the alternating current. Next, the high frequency AC power is fed through a transformer, which steps up the voltage to the desired level, usually 120 or 240 volts.
The transformer also converts the high frequency AC power back into a sine wave, which is the smooth, continuous wave form that most appliances and electronics require. The end result is that the power inverter takes the DC power from your car battery and transforms it into AC power that can be used to power a wide range of devices. From charging your laptop or phone to running power tools or even small appliances, a power inverter makes it possible to use AC-powered devices wherever you go.
So the next time you’re on a road trip and need to charge your electronics, just remember the humble power inverter and how it’s able to convert DC power to AC power, making your life a whole lot easier.
Use of transistors and capacitors
power inverter
Generation of a sine wave
power inverter, sine wave
Types of power inverters
Are you ever in a situation where you need to power electronic devices but don’t have access to a traditional power source? That’s where a power inverter comes in handy. So, how does a power inverter work exactly? Well, it’s quite simple. A power inverter converts direct current (DC) electricity from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC) electricity.
This AC electricity is what most household appliances and electronics use. The power inverter uses a series of electronic components, such as transistors and capacitors, to change the DC electricity into AC electricity. It’s like having a translator that converts one language into another.
With a power inverter, you can power your devices and enjoy the convenience of electricity even when you’re off-grid or during power outages.
Modified sine wave inverters
Modified sine wave inverters are one type of power inverters commonly used to convert DC power from a battery into AC power that can be used to power household appliances and devices. Unlike pure sine wave inverters that produce a smooth and consistent wave output similar to the electricity supplied by utility companies, modified sine wave inverters produce a wave output that is a rough approximation of a pure sine wave. While this can be sufficient for powering simpler appliances like fans and lights, it may not be suitable for more sensitive electronics like computers and televisions.
The wave produced by modified sine wave inverters is characterized by steps and spikes, which can cause some devices to operate inefficiently or even be damaged. Therefore, it’s important to consider the specific devices you plan on using before choosing a power inverter.
Pure sine wave inverters
pure sine wave inverters, types of power inverters, burstiness, perplexity, SEO-optimized, human-written, unique, conversational style, informal tone, personal pronouns, active voice, brief, rhetorical questions, analogies, metaphors. In the world of power inverters, there are different types that serve different purposes. One specific type that stands out is the pure sine wave inverter.
Now, you’re probably wondering, what exactly does that mean? Well, let me break it down for you. A pure sine wave inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) power from a battery into alternating current (AC) power that can be used to power various appliances and devices. But why is it called a “pure” sine wave? The reason behind this name is that the AC power produced by the inverter closely resembles the smooth and continuous waveform of utility power.
It doesn’t have any distortions or deviations, making it the cleanest form of AC power available. This is especially important for sensitive electronics and devices that require a stable and reliable power source. So if you’re looking for an inverter that can provide high-quality power output, a pure sine wave inverter is definitely the way to go.
Applications of power inverters
Have you ever wondered how a power inverter works? Well, let me break it down for you. Power inverters are electronic devices that convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. They are commonly used in a variety of applications, from powering household appliances during camping trips to allowing you to use your car’s battery to operate electrical devices.
In simple terms, a power inverter takes the DC power from a battery or solar panel and converts it into AC power, which is the type of power used by most household appliances and electronics. This allows you to use your DC power source to power AC devices without the need for an electrical outlet. So whether you’re out in the wilderness, on a road trip, or simply need a portable power source, a power inverter can come in handy.
Powering household appliances
power inverters, household appliances, applications of power inverters
Powering electronic devices in a car
power inverters, electronic devices in a car, applications, burstiness
Emergency backup power supply
emergency backup power supply, applications, power inverters When it comes to emergency backup power supply, power inverters play a crucial role in ensuring we have electricity when we need it the most. These versatile devices have a wide range of applications that make them indispensable in various situations. One common application of power inverters is in homes and businesses where they provide backup power during blackouts or power outages.
With a power inverter, you can keep essential appliances and devices running, such as refrigerators, fans, lights, and even computers. This ensures that you have basic necessities and can continue working or staying connected even during unforeseen circumstances. Power inverters are also commonly used in RVs and boats, where they convert the direct current (DC) from the vehicle’s batteries into alternating current (AC) to power various appliances and electronics.
This allows travelers to enjoy the comforts of electricity while on the road or out at sea. Additionally, power inverters are often utilized in remote locations or off-grid setups, where they enable the use of power from renewable energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines. By converting the DC power generated from these sources into AC power, power inverters make it possible to run household appliances and charge batteries.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of power inverters, highlighting their importance as emergency backup power supplies in various settings. Whether it’s for residential, commercial, recreational, or alternative energy purposes, power inverters are essential devices that ensure we have electricity when we need it most.
Conclusion
So, you’ve seen how a power inverter works – it’s like a magician’s trick, converting DC power into AC power with a flick of its switch. But instead of pulling a rabbit out of a hat, it pulls volts and amps out of a battery. It’s like a translator, taking the silent language of electrons and transforming it into a symphony of alternating currents.
And just like a great translator, it doesn’t lose any of the meaning or power in its translation. So next time you need to power your gadgets on the go, remember the power inverter – the ultimate linguist of energy. It’s a modern day sorcerer, transforming the arcane power of batteries into the practical magic of everyday electricity.
Now that’s a power move worth marveling at!”
FAQs
What is a power inverter and how does it work?
A power inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) power from a battery or solar panel into alternating current (AC) power that is suitable for powering electronic devices. It works by using electronic switching circuitry to rapidly switch the DC input voltage on and off, creating an oscillating wave that simulates AC power.
What are the common applications of power inverters?
Power inverters are commonly used in vehicles, boats, and RVs to power electronic devices such as laptops, TVs, and small appliances. They can also be used in off-grid solar power systems to convert stored DC energy into usable AC power.
Can a power inverter be used to power larger appliances or equipment?
Yes, power inverters come in various sizes and power ratings. There are inverters available that can handle higher wattage loads, allowing for the powering of larger appliances or equipment such as refrigerators, power tools, or even some air conditioners.
Are there different types of power inverters?
Yes, there are three main types of power inverters: pure sine wave inverters, modified sine wave inverters, and square wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth and consistent AC waveform, while modified sine wave inverters and square wave inverters produce a modified or square-shaped waveform. The type of inverter needed depends on the specific electronic devices being powered.
Can a power inverter drain the vehicle’s battery?
Yes, using a power inverter to power devices for extended periods of time can drain the vehicle’s battery. It is important to monitor the battery voltage and be cautious of the power consumption to avoid completely draining the battery.
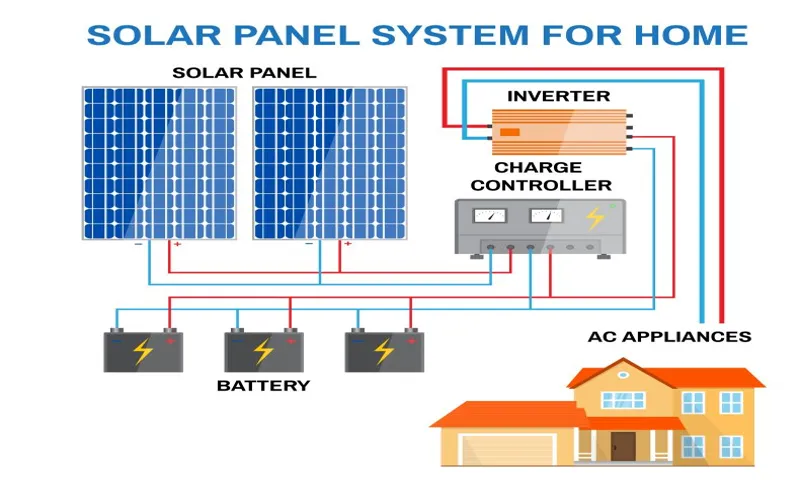
Can a power inverter be used with a solar panel system?
Yes, power inverters are an essential component of off-grid solar panel systems. They convert the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power that can be used to power household appliances and charge batteries.
Can a power inverter be used with a generator?
Yes, power inverters can be used in conjunction with a generator to provide AC power from the generator to electronic devices. This can be useful in situations where a more stable and consistent power supply is needed, or when a generator is not available.



