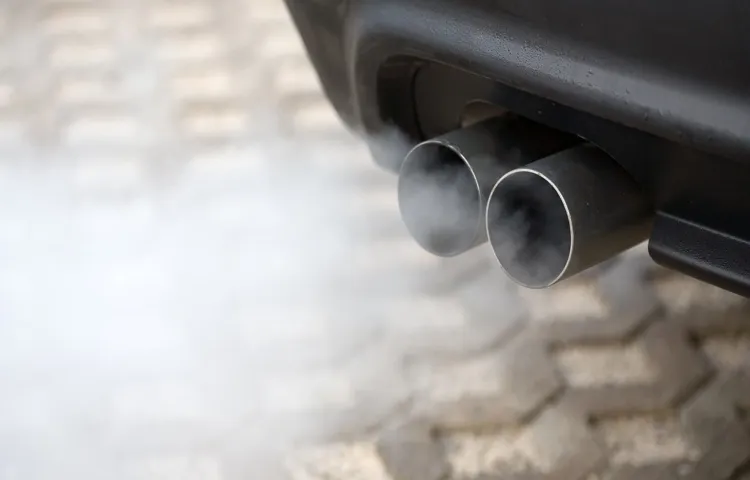
Have you ever wondered what happens when coolant gets into the exhaust? It’s a question that many car owners may not have thought about, but it’s an important one to understand. Coolant is a vital component of your car’s cooling system, helping to regulate the temperature of the engine and prevent overheating. But when coolant finds its way into the exhaust system, things can go downhill fast.
Imagine your car’s cooling system as a well-oiled machine, working seamlessly to keep the engine running at the right temperature. The coolant circulates through the engine, absorbing heat and carrying it away to be released through the radiator. It’s a delicate balance that keeps your engine running smoothly and prevents it from overheating.
However, if there is a leak or a problem with the engine or cooling system, coolant can escape and find its way into the exhaust system. This is where things can take a turn for the worse. When coolant mixes with the hot exhaust gases, it creates a toxic mixture that can have serious consequences for your car’s performance.
One of the most immediate effects of coolant entering the exhaust is a decrease in engine performance. When coolant mixes with the fuel in the combustion chamber, it can lead to incomplete combustion, causing the engine to run rough, misfire, or even stall. This can result in a loss of power and acceleration, making it harder to drive your car.
Another issue that can arise from coolant in the exhaust is the production of white smoke. This smoke is a clear indication that something is not right with your engine. The coolant mixing with the hot exhaust gases creates a steam-like vapor that is expelled through the tailpipe, creating a cloud of white smoke.
If you notice this smoke coming from your car’s exhaust, it’s time to take it to a mechanic as soon as possible. In addition to decreased performance and white smoke, coolant in the exhaust can also lead to damage to the catalytic converter. This important component helps to reduce harmful emissions from the exhaust gases.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever wondered what would happen if coolant got into the exhaust? Well, it’s not a pleasant scenario, that’s for sure. Coolant is a liquid that is used in the cooling system of a car to prevent the engine from overheating. If coolant were to somehow find its way into the exhaust system, it could potentially cause a lot of damage.
The coolant would mix with the exhaust gases and create a thick, white smoke that would be emitted from the tailpipe. This kind of smoke is a sign that something is seriously wrong with the engine and should not be ignored. In addition to the smoke, coolant in the exhaust can also lead to a loss of engine power and a decrease in fuel efficiency.
It’s important to address this issue as soon as possible, as continued driving with coolant in the exhaust can cause further damage to the engine.
What is coolant?
Coolant is a substance that is commonly used in various machines and engines to regulate and maintain the temperature. It plays a vital role in preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. Think of coolant as the body’s equivalent of sweating.
When we exercise or are exposed to hot temperatures, our bodies naturally produce sweat to cool down. Similarly, coolant acts as the cooling agent for machines and engines. It circulates through the system, absorbing heat and carrying it away to prevent any damage or malfunction.
Without coolant, machines can overheat, leading to potential breakdowns and costly repairs. Coolant is typically a mixture of water and antifreeze, which helps to lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of the liquid. Additionally, coolant contains additives that prevent corrosion, lubricate moving parts, and protect against cavitation (the formation of air bubbles that can damage components).
In summary, coolant is an essential component in keeping machines and engines running smoothly and efficiently.
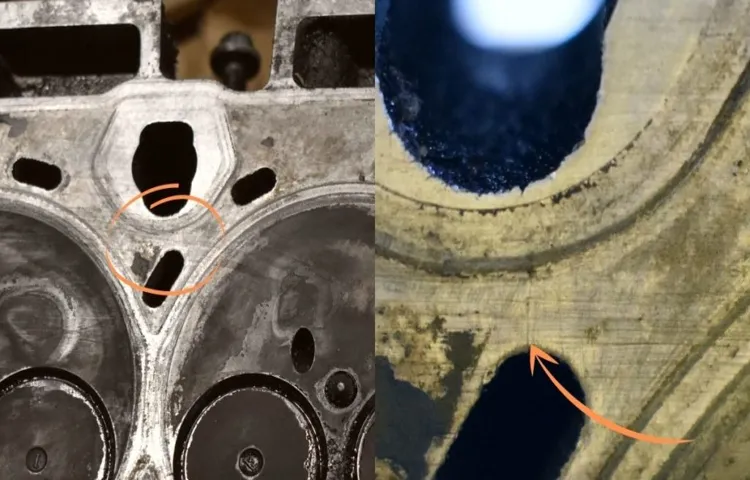
What is the exhaust system?
exhaust system
How can coolant get into the exhaust?
In some cases, coolant can find its way into the exhaust system of a vehicle, causing a range of issues. But how does this happen? Well, it typically occurs when there is a problem with the engine’s cooling system. The cooling system is responsible for regulating the temperature of the engine and preventing it from overheating.
However, if there is a leak or a malfunction in the cooling system, coolant can enter the exhaust system. This can happen through various routes, such as a cracked cylinder head, a faulty head gasket, or a damaged intake manifold gasket. Once the coolant enters the exhaust system, it mixes with the hot gases and produces steam or white smoke, which can be seen coming out of the tailpipe.
This can be a serious issue that needs to be addressed promptly, as it can lead to engine damage and reduced performance.
Effects of Coolant in the Exhaust
Have you ever wondered what would happen if coolant got into the exhaust? Well, it’s not a good scenario. Coolant is not supposed to be in the exhaust system, and if it does get in there, it can cause some serious issues. One of the first things you might notice is a white or bluish smoke coming out of the tailpipe.
This is a sign that coolant is burning along with the fuel, and it can indicate a leaking head gasket or a cracked cylinder head. Not only is this smoke unsightly, but it can also be harmful to breathe in. Another problem that coolant in the exhaust can cause is engine overheating.
Coolant is responsible for keeping the engine temperature regulated, so if it is leaking into the exhaust system, it won’t be able to do its job. This can lead to the engine overheating, which can cause significant damage and potentially even engine failure. So, if you ever notice coolant in your exhaust, it’s important to address the issue as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your vehicle.
Corrosion
coolant, exhaust, corrosion, effects
Loss of coolant
effects of coolant in the exhaust
Reduced engine performance
reduced engine performance, coolant in the exhaust, effects of coolant in the exhaust When it comes to vehicle performance, having a well-maintained engine is crucial. However, there can be various factors that can affect engine performance, and one of them is coolant in the exhaust. Coolant is a liquid that helps regulate the temperature of the engine and prevents it from overheating.
But when coolant finds its way into the exhaust system, it can cause a series of problems that can lead to reduced engine performance. One of the effects of coolant in the exhaust is the formation of a white or grayish smoke coming out of the tailpipe. This smoke can be an indication that coolant is leaking into the combustion chamber and being burned along with the fuel.
When this happens, the coolant can dilute the fuel mixture, leading to incomplete combustion and reduced power output. Additionally, coolant in the exhaust can also cause damage to the engine’s internal components. The coolant, when mixed with the hot exhaust gases, can form a corrosive mixture that can eat away at the engine’s valves, pistons, and other vital parts.
This can result in poor compression, loss of power, and even engine failure if left untreated. Furthermore, coolant in the exhaust can also lead to increased fuel consumption. When coolant is leaking into the combustion chamber, it can alter the air-fuel ratio, causing the engine to run rich.
A rich fuel mixture means that there is an excessive amount of fuel compared to the amount of air, resulting in increased fuel consumption and poor fuel efficiency. In conclusion, the presence of coolant in the exhaust can have detrimental effects on engine performance. From the formation of smoke to damage to internal components and increased fuel consumption, coolant leakage in the exhaust should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage to the engine.
Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify and resolve any coolant-related issues before they escalate into more significant problems. Remember, a well-maintained engine is a powerful engine. So, if you notice any signs of coolant in the exhaust, it’s best to get it checked out by a professional mechanic as soon as possible.
Dangers of Coolant in the Exhaust
If coolant were to make its way into the exhaust system of a vehicle, it could lead to some serious issues. Coolant is primarily used in the engine to help regulate temperature and prevent overheating. However, if it were to leak into the exhaust, it could cause a number of problems.
One of the main concerns is that coolant is not designed to be burned. When coolant is exposed to the high temperatures of the exhaust system, it can create a white smoke, which is a clear indication that something is wrong. This white smoke can be toxic and harmful to both the environment and anyone who is nearby.
Additionally, coolant in the exhaust can also damage the catalytic converter, which plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions. In some cases, coolant in the exhaust can even lead to engine damage, as it can cause the engine to misfire or stall. Overall, if coolant were to get into the exhaust, it would be important to address the issue quickly to prevent further damage and ensure the safety of both the vehicle and its occupants.
Fire hazard
Fire hazard, coolant, exhaust, danger When it comes to vehicle maintenance and safety, it’s important not to overlook the potential dangers of coolant in the exhaust. Coolant, or antifreeze, is a critical component of your vehicle’s engine cooling system. It helps regulate the temperature of the engine, preventing it from overheating.
However, if coolant leaks into the exhaust system, it can pose a serious fire hazard. The exhaust system of a vehicle is designed to safely expel harmful gases and fumes created during the combustion process. These gases are extremely hot, and if coolant comes into contact with them, it can ignite and start a fire.
This is especially true if the coolant leaks near the catalytic converter, which can reach temperatures of up to 1,200 degrees Fahrenheit. The danger of coolant in the exhaust is not only limited to the potential for fire. Coolant contains chemicals that can be toxic when inhaled, and if it enters the cabin of the vehicle, it can pose a serious health risk to the occupants.
In addition, coolant leaks can lead to engine damage and reduced performance if not addressed promptly. To prevent coolant from entering the exhaust system, it’s important to regularly inspect and maintain your vehicle’s cooling system. Look for signs of coolant leaks, such as puddles under the vehicle or a sweet smell coming from the engine.
If you suspect a leak, have it repaired immediately by a qualified mechanic. In conclusion, the dangers of coolant in the exhaust should not be underestimated. It can pose a serious fire hazard and health risk if not addressed promptly.
Regular maintenance and inspection of your vehicle’s cooling system is key to preventing coolant leaks and ensuring the safety of yourself and your passengers.
Toxic fumes
Toxic fumes from a car’s exhaust can be hazardous to our health, but did you know that there are also dangers lurking in the coolant? Coolant, or antifreeze, is a crucial component of a car’s cooling system, keeping the engine from overheating. However, when coolant mixes with the exhaust, it can create toxic fumes that can be harmful to both humans and the environment. These fumes contain harmful chemicals, such as ethylene glycol, which is poisonous if ingested or inhaled.
Inhaling these fumes can cause respiratory problems, nausea, dizziness, and even death. Additionally, the toxins released from coolant can also contaminate the air and contribute to pollution. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the coolant system in your car is functioning properly and that there are no leaks or malfunctions that could lead to the mixing of coolant and exhaust gases.
Regular maintenance and inspections of your vehicle’s cooling system can help minimize the risk of exposure to these dangerous fumes and protect your health.
Damage to other components
coolant in the exhaust, dangers of coolant in the exhaust, damage to other components. Exposing your vehicle’s engine to extreme temperatures can cause a host of problems, but one issue that often goes unnoticed is the danger posed by coolant in the exhaust. Coolant, also known as antifreeze, is a vital component in your vehicle’s cooling system, and it helps regulate the engine temperature.
However, if coolant finds its way into the exhaust system, it can cause serious damage to other components. One of the primary dangers of coolant in the exhaust is the potential for engine damage. When coolant enters the exhaust system, it can mix with the hot gases and cause them to solidify.
This can result in a buildup of solid material, known as carbon deposits, within the exhaust pipes and muffler. These deposits can restrict the flow of exhaust gases, leading to poor engine performance and decreased fuel efficiency. Additionally, coolant in the exhaust can corrode other components of the exhaust system.
The presence of coolant can cause metal parts to rust and weaken over time. This can lead to cracks and leaks in the exhaust pipes and muffler, which can result in increased noise and emissions. Moreover, the corrosive nature of the coolant can also damage oxygen sensors and catalytic converters, which are critical for reducing harmful emissions.
Furthermore, coolant in the exhaust can have a detrimental effect on the engine’s combustion process. When coolant mixes with the hot gases in the exhaust, it can create conditions that are not conducive to efficient combustion. This can result in decreased engine power, rough idling, and increased exhaust emissions.
It can also lead to an overheating engine, as the coolant is not able to effectively cool the engine due to its presence in the exhaust system. In conclusion, coolant in the exhaust poses several dangers to your vehicle’s engine and exhaust system. From engine damage to corrosion and decreased combustion efficiency, the effects of coolant in the exhaust can be significant.
Steps to Fix Coolant in the Exhaust
Imagine this scenario: you start up your car in the morning and notice a strange smell coming from the exhaust. You might be wondering, “What would happen if coolant got into the exhaust?” Well, it’s not a good sign. When coolant enters the exhaust system, it can result in a few different issues.
First of all, it can cause white smoke to come out of the tailpipe. This is a clear indication that coolant is burning and being released as steam. Additionally, coolant in the exhaust can lead to overheating problems in the engine.
The coolant is meant to help regulate the engine’s temperature, so when it’s not circulating properly, the engine can quickly become too hot. This can cause damage to the internal components and potentially lead to engine failure. So, if you suspect that coolant has made its way into your exhaust, it’s important to have it inspected and repaired as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Diagnose the problem
coolant in the exhaust
Repair or replace the affected parts
coolant in the exhaust, repair, replace, affected parts
Flush the coolant system
flush the coolant system, fix coolant in the exhaust Are you experiencing coolant in your exhaust? This can be a frustrating problem, but luckily, there are steps you can take to fix it. One of the first things you should do is flush the coolant system. Over time, your coolant system can become contaminated with debris and other impurities.
This can lead to coolant leaking into the exhaust and causing problems. By flushing the coolant system, you can remove these contaminants and restore the proper flow of coolant. To flush the system, start by draining the coolant from the radiator.
Then, refill the system with a mixture of water and radiator flush solution. Run the engine for a few minutes to circulate the solution, and then drain it again. Finally, refill the system with fresh coolant and water.
This process can help remove any buildup in the coolant system and fix the issue of coolant in the exhaust.
Test for coolant leaks
coolant leaks, fix coolant in exhaust. If you suspect that you have coolant leaks in your car, it’s important to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage. One common symptom of coolant leaks is finding coolant in your exhaust.
When coolant leaks into the exhaust system, it can cause a variety of problems, including engine overheating and a decrease in performance. To fix coolant in the exhaust, you can follow a few simple steps. First, identify the source of the coolant leak.
This may require inspecting the radiator, hoses, and water pump for any signs of damage or wear. Once the leak has been located, you can replace or repair the affected component. If the leak is coming from a hose, for example, you can replace it with a new one.
Additionally, it’s important to check the coolant level in your car and top it off if necessary. This will help prevent further leaks and ensure that your engine stays cool. In some cases, it may be necessary to flush the entire cooling system to remove any contaminants and improve its performance.
By following these steps and addressing coolant leaks promptly, you can keep your car running smoothly and prevent costly repairs down the line.
Conclusion
If coolant were to somehow invade the sacred territory of the exhaust, chaos would ensue in the automotive realm. The coolant, like a mischievous prankster, would eagerly mingle with the hot gases in the exhaust system, creating a symphony of chemical reactions that would undoubtedly result in mayhem. Firstly, the coolant, oblivious to its unwelcome intrusion, would react with the intense heat of the exhaust pipes.
As the temperature rises, the coolant would transform into a sizzling vapor, creating billowing clouds reminiscent of an enthusiastic steam locomotive. Oh, the drama! This steamy affair would not go unnoticed by the exhaust gases, who would react with indignant fervor. The gases, a rowdy bunch radiating with energy, would engage in a fierce battle with the coolant vapor.
Their fierce confrontation would cause turbulence in the exhaust system, leading to a tumultuous uproar of hisses, pops, and bangs. While this showdown unfolds in the exhaust pipes, the engine would certainly be throwing a tantrum of its own. The coolant, typically contained within its designated cooling system, would wreak havoc by infiltrating places it should never venture.
The engine, startled by this unexpected visit, would show its displeasure through erratic behavior, perhaps introducing misfires, overheating, or even an outright revolt against such an outrageous intrusion. Amidst this chaotic scene, the exhaust backpressure would skyrocket, creating a conundrum for the poor engine. Like trying to breathe through a clogged nostril, the engine would struggle to exhale, its performance hindered, and its power diminished.
Oh, the frustration! In the end, the pairing of coolant and exhaust is no dazzling fusion but a disastrous collision. The once harmonious orchestra under the hood transforms into a cacophony of malfunctioning mechanical elements struggling to find their rhythm. It serves as a vivid reminder that, much like in life, some things are simply not meant to mix.
So, my dear friends, let us be grateful for the separation between the coolant and the exhaust. The harmony of a well-functioning engine rests upon this delicate balance. And if, by some unfortunate twist of fate, the coolant decides to venture where it doesn’t belong, be prepared for an automotive spectacle that would surely make even the most stoic mechanic shed a tear.
Prevention is key
coolant in the exhaust, fix coolant in the exhaust
Regular maintenance is important
coolant in the exhaust, regular maintenance, fix, steps, importance
Seek professional help if needed
coolant in the exhaust
FAQs
What are the potential consequences of coolant getting into the exhaust system?
When coolant enters the exhaust system, it can cause damage to the catalytic converter, leading to reduced engine performance and increased emissions. It can also result in the production of white smoke from the tailpipe and a sweet smell in the exhaust.
How does coolant get into the exhaust system?
Coolant can enter the exhaust system through a variety of ways, such as a blown head gasket, a cracked cylinder head, or a faulty coolant seal. It is important to address any coolant leaks promptly to prevent contamination.
Can coolant in the exhaust cause engine overheating?
Yes, coolant in the exhaust can contribute to engine overheating. As the coolant is not properly circulating through the engine, it cannot effectively cool it down. This can lead to increased engine temperatures and potential damage if not addressed.
What are the symptoms of coolant in the exhaust system?
Some common symptoms of coolant in the exhaust system include white smoke coming from the tailpipe, a sweet smell in the exhaust, engine misfires, reduced engine performance, and higher than usual coolant consumption.
What should I do if I suspect coolant is getting into the exhaust?
If you suspect coolant is entering your exhaust system, it is important to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic. They will be able to diagnose the issue and determine the best course of action, which may include repairing the source of the coolant leak.
Is it safe to drive with coolant in the exhaust?
It is generally not recommended to drive with coolant in the exhaust. This can lead to engine damage and potential overheating issues. It is best to have the issue addressed promptly to avoid further complications.
Can coolant in the exhaust cause damage to the O2 sensors?
Yes, coolant in the exhaust system can damage the O2 sensors. The coolant can contaminate the sensors and cause them to provide inaccurate readings, resulting in poor engine performance and increased emissions. It is important to replace any damaged O2 sensors if coolant has been present in the exhaust system.



